Diving in a kelp forest in Monterey Bay recently, I watched a tubby 200-pound harbor seal follow a fellow diver, nibbling on his flippers. The diver, a graduate student, was using sponges to collect DNA samples from the ocean floor. Curious seals, he told me, can be a nuisance. When he bags his sponges and places them in his collection net, they sometimes bite into them, puncturing the bags and spoiling his samples.
Under the Marine Mammal Protection Act, coming closer than 50 yards to seals and dolphins is considered harassment, but they’re free to harass you, which seems only fair given the centuries of deadly whaling and seal hunting that preceded a generational shift in how we view the world around us.
The shift took hold in 1969, the year a massive oil spill coated the Santa Barbara coastline and the Cuyahoga River, in Cleveland, caught fire. Those two events helped spark the first Earth Day, in 1970, and the shutdown of America’s last whaling station in 1971. Protecting the environment from pollution and from loss of wilderness and wildlife quickly moved from a protest issue to a societal ethic as America’s keystone environmental legislation was passed at around the same time, written by a Democratic Congress and signed into law by a Republican president, Richard Nixon.
Those laws include the National Environmental Policy Act (1969) , the Clean Air Act (1970), the Clean Water Act (1972) and the Marine Mammal Protection Act (1972), which goes further than the Endangered Species Act (1973) in protecting all marine mammals, not just threatened ones, from harassment, killing or capture by U.S. citizens in U.S. waters and on the high seas.
All these “green” laws and more are under attack by the Trump administration, its congressional minions and longtime corporate opponents of environmental protections, including the oil and gas industry. Republicans’ disingenuous argument for weakening the Endangered Species Act and the Marine Mammal Protection Act is that the legislation has worked so well in rebuilding wildlife populations that it’s time to loosen regulations for a better balance between nature and human enterprise. When it comes to marine mammal populations, that premise is wrong.
On July 22, at a House Natural Resources subcommittee meeting, Republican Rep. Nick Begich of Alaska introduced draft legislation that would scale back the Marine Mammal Protection Act. Among other things, his proposal would limit the ability of the federal government to take action against “incidental take,” the killing of whales, dolphins and seals by sonic blasts from oil exploration, ship and boat strikes or by drowning as accidental catch (also known as bycatch) in fishing gear. Begich complained that marine mammal protections interfere with “essential projects like energy development, port construction, and even fishery operations.”
Rep. Jared Huffman (D-San Rafael), the ranking member on the House Resources Committee, calls the legislation a “death sentence” for marine mammals.
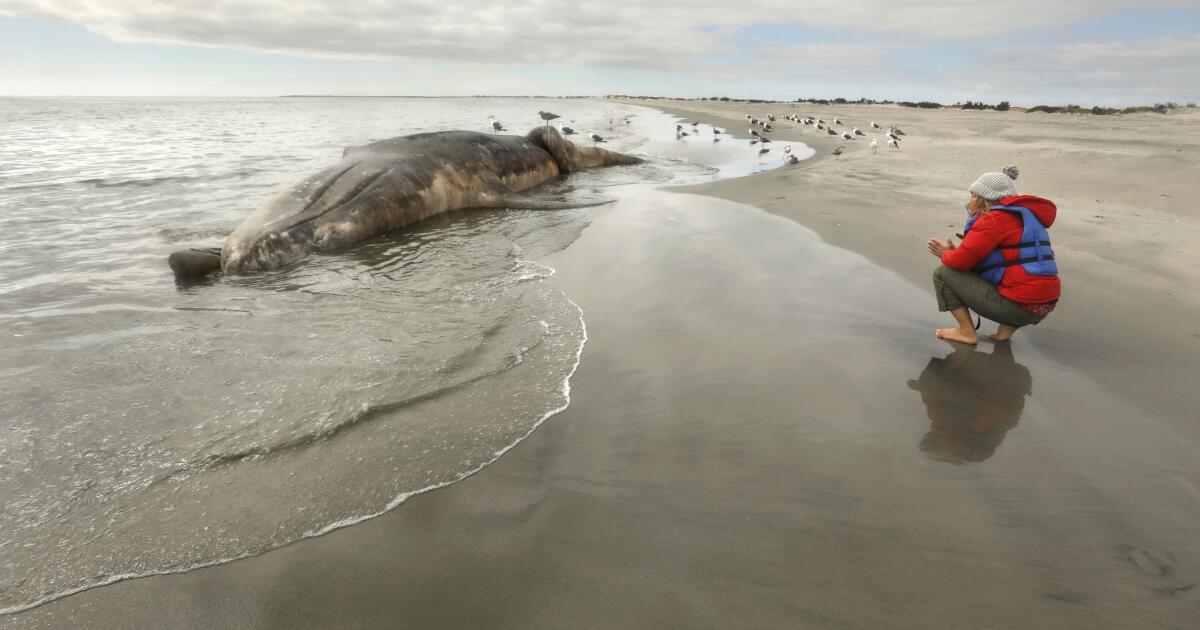
It’s true that the marine mammal law has been a success in many ways. Since its passage, no marine mammal has gone extinct and some species have recovered dramatically. The number of northern elephant seals migrating to California beaches to mate and molt grew from 10,000 in 1972 to about 125,000 today. There were an estimated 11,000 gray whales off the West Coast when the Marine Mammal Protection Act became law; by 2016, the population peaked at 27,000.
But not all species have thrived. Historically there were about 20,000 North Atlantic right whales off the Eastern Seaboard. They got their name because they were the “right” whales to harpoon — their bodies floated for easy recovery after they were killed. In 1972 they were down to an estimated 350 individuals. After more than half a century of federal legal protection, the population is estimated at 370. They continue to suffer high mortality rates from ship strikes, entanglement in fishing gear and other causes, including noise pollution and greater difficulty finding prey in warming seas.
Off Florida, a combination of boat strikes and algal pollution threaten some 8,000-10,000 manatees. The population’s recovery (from about 1,000 in 1979) has been significant enough to move them off the endangered species list in 2017, but since the beginning of this year alone, nearly 500 have died. Scientists would like to see them relisted, but at least they’re still covered by the Marine Mammal Protection Act.
A 2022 study in the Gulf of Mexico found that in areas affected by the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill 12 years earlier, the dolphin population had declined 45% and that it might take 35 years to recover. In the Arctic Ocean off Alaska, loss of sea ice is threatening polar bears (they’re considered marine mammals), bowhead and beluga whales, walruses, ringed seals and harp seals.
On the West Coast the number of gray whales — a Marine Mammal Act success story and now a cautionary tale — has crashed by more than half in the last decade to fewer than 13,000, according to a recent report by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA, the nation’s lead ocean agency, is an endangered species in its own right in the Trump era). Declining prey, including tiny shrimp-like amphipods, in the whales’ summer feeding grounds in the Arctic probably caused by warming water are thought to be a major contributor to their starvation deaths and reduced birth rates.
The whale’s diving numbers are just one signal that climate change alone makes maintaining the Marine Mammal Act urgent. Widespread marine heat waves linked to a warming ocean are contributing to the loss of kelp forests that sea otters and other marine mammals depend on. Algal blooms off California, and for the first time ever, Alaska, supercharged by warmer waters and nutrient pollution, are leading to the deaths of thousands of dolphins and sea lions.
What the Trump administration and its antiregulation, anti-environmental-protection supporters fail to recognize is that the loss of marine mammals is an indicator for the declining health of our oceans and the natural world we depend on and are a part of. This time, saving the whales will be about saving ourselves.
David Helvarg is executive director of Blue Frontier, an ocean policy group. His next book, “Forest of the Sea: The Remarkable Life and Imperiled Future of Kelp,” is scheduled to be published in 2026.